Why many companies choose frequency inverters over servo controllers
- Drive Technology
- 22.8.2025
- Reading Time: {{readingTime}} min

Contents
Industrial automation is constantly evolving—and with it, the demands on drive systems. While simple speed controls were sufficient a few decades ago, modern applications increasingly require complex, highly accurate, and energy-efficient solutions. Frequency inverters are still standard in many industries. However, increasing demands on efficiency, product quality, and process control are making servo controllers increasingly important. Nevertheless, their use remains focused on certain high-end applications. Why is this the case? And is it worth switching? If so, when?
This article highlights the differences between frequency inverters and servo drives, lists the advantages and disadvantages of both systems, and specifically addresses the questions and concerns that many companies have when it comes to converting to servo technology.
Frequency inverters – The proven choice for many applications
Frequency inverters offer a flexible solution for a wide range of applications. They enable speed control for asynchronous motors and also for certain synchronous motors. They are particularly popular in areas where simple speed control is sufficient, such as pumps, blowers, or conveyor belts.
Advantages of frequency inverters:
- Cost savings: Low investment and maintenance costs.
- Robustness: Ideal for simple motion profiles without high precision requirements and well suited for harsh operating conditions.
- Easy implementation: Established for decades, with a broad base of skilled workers.
Servo controllers – The more precise alternative
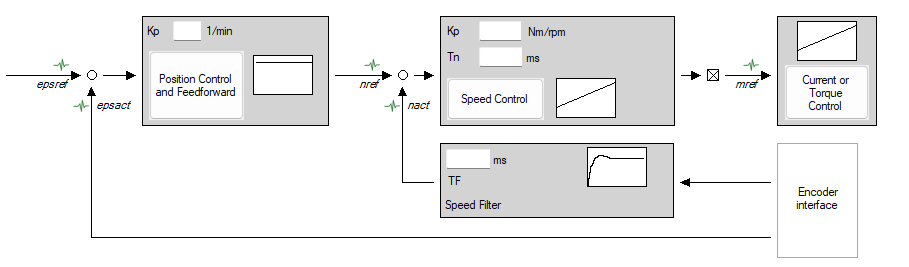
Servo drives are specially designed for applications that require precise position, torque, or speed control. They act as the “brain” of the drive system: they process feedback from sensors, compare it with the setpoints, and adjust the motor movement accordingly.
Advantages of servo controllers:
- High precision: Ideal for demanding motion profiles with rapid direction changes, such as in pick-and-place applications, palletizing, and dosing systems.
- Better energy efficiency: Thanks to the precise control of torque, speed, and position, only as much energy is used as is actually needed.
- Increased process stability: Thanks to the closed control loops, deviations are compensated in real-time — this ensures constant motion sequences and consistent workpiece quality.
Frequently asked questions about servo controllers
When companies consider switching to servo technology, the following questions often arise:
Are servo drives really more economical than frequency inverters?
The investment costs are higher, but servo drives can pay for themselves in the long term thanks to more precise control and lower energy consumption. The additional energy savings achieved by using servo systems instead of frequency inverter solutions are typically between 7 % and 10 %, but can be as high as 50 % depending on the type of gearbox. The added value is particularly significant in applications with many process changes and frequent partial loads.
How complex is it to integrate servo controllers into existing systems?
The complexity of the transition depends on the existing infrastructure. Modern servo systems can often be easily connected to existing control systems. However, in many cases, integration requires precise adaptation of the software and coordination of the interfaces. Mechanical aspects, such as fastenings or coupling elements, must also be taken into account.
Do we need special expertise to operate servo controllers?
Yes, servo drives require a different approach than frequency inverters, but with targeted training, technicians can quickly transition to the new system. For a standard application, you can expect 1.5 days of basic training per person.
Which applications benefit most from servo controllers?
Wherever multiple axes are installed in a control cabinet, particularly in mechanical engineering, robotics, packaging technology, and precision manufacturing processes, the advantages of servo technology really pay off.
Are there any subsidies available for switching to energy-efficient drives?
Yes, many countries have programs to promote energy-efficient technologies. It is worth searching specifically for subsidies.
Are there any differences between inverter systems and servo drives in terms of maintenance?
Both are maintenance-free. The servo drive can use the process signals (currents, speed, position) to provide information about the wear status of the connected mechanics and report this to the overlaid control system, enabling predictive maintenance.
Is a servo controller perhaps “oversized” for our application?
Servo drives are particularly worthwhile when high dynamics, precision, or energy efficiency are required. For simple applications, such as simple conveyor drives, pumps, and blowers, frequency inverters are usually the more economical choice. Here, up to 50% of investment costs can be saved.
Can servo drives also be used for simple applications?
Yes, many modern servo drives are scalable and can also be used for simple motion sequences. This can be particularly useful in terms of energy efficiency or integration into digital control concepts.
What do I need to consider when selecting a servo drive system?
Important factors include power requirements, desired connection to the higher-level control system via fieldbus (e.g., EtherCAT, CANopen, PROFINET), environmental conditions, cycle times, and mechanical requirements. A close cooperation with the manufacturer helps to find the optimal solution.
Why do many companies continue to use frequency inverters?
Although servo controllers offer many technical advantages, there are several reasons why companies often decide against switching:
- Cost concerns: Servo drives are more expensive to purchase than frequency inverters. In addition, there are additional training costs for personnel.
- Complexity of changeover: Existing systems are often designed for frequency inverters, and changeover may require significant infrastructure adjustments.
- Technical barriers: Many companies do not have the same level of expertise in servo drive technology as they do in frequency inverters. The fear of more complicated commissioning deters many users.
- Proven processes: When a system has been in place for years, people often wonder why it should be changed.
Where does the use of servo technology make sense?
The decision between frequency inverter and servo drive is rarely a blanket one and depends heavily on the application. Inverter systems offer a cost-effective, robust, and easy-to-integrate solution for simple applications without high demands on precision or dynamics. They remain an established technology with a broad user base and easy maintenance.
Servo drives, on the other hand, are state-of-the-art and enable a significant increase in performance in many industrial processes thanks to their precise control and high efficiency. The use of servo technology is a future-proof solution, especially in areas where speed, energy savings, and product quality are crucial. The higher acquisition costs are often compensated by savings in operation and higher production quality.
When is a switch worthwhile?
It is crucial to take a conscious look at specific needs, existing infrastructure, and long-term goals. Companies that want to increase their competitiveness should consider whether the use of servo drives is exactly the factor that will give them the decisive advantage. Those who invest early can gain long-term benefits — technologically, economically, and ecologically.
Are you considering switching to servo technology – or are you already facing a concrete decision? As an experienced automation partner, we support you in developing customized drive solutions and integrating them efficiently into existing or new machine concepts. Whether retrofitting or new installation: we accompany you from the initial concept to series production – technically profound, hands-on, and with your long-term goals in mind.